One good way to monitor your container status is to use Docker’s HEALTHCHECK feature.
As part of testing the followed actions upon an unhealthy container, I had to experiment how this works. I wrote a small Go app that replies to /health requests, and the status it responds is configurable.
The webserver listens on $PORT (defaults to 8080). To change its status, simply make an api call to one of the supported actions. You can either connect the container to execute it, or if you have mapped a port on the host, you can use it.
Supported actions are:
- /sabotage will make it respond with 500.
- /timeout will make it respond after 20s.
- /recover will return it back to healthy state, with 200 response code.
You can find the source code here.
From the Docker docs -
| |
The options that can appear before CMD are:
--interval=DURATION (default: 30s)
--timeout=DURATION (default: 30s)
--start-period=DURATION (default: 0s)
--retries=N (default: 3)
You can configure the HEALTHCHECK settings in the Dockerfile or the docker-compose.yml. In my example, I use it in the Dockerfile.
Demo
Clone the repo and build the image:
docker build . -t go-healthcheckerBring up the container, wait until it gets healthy.
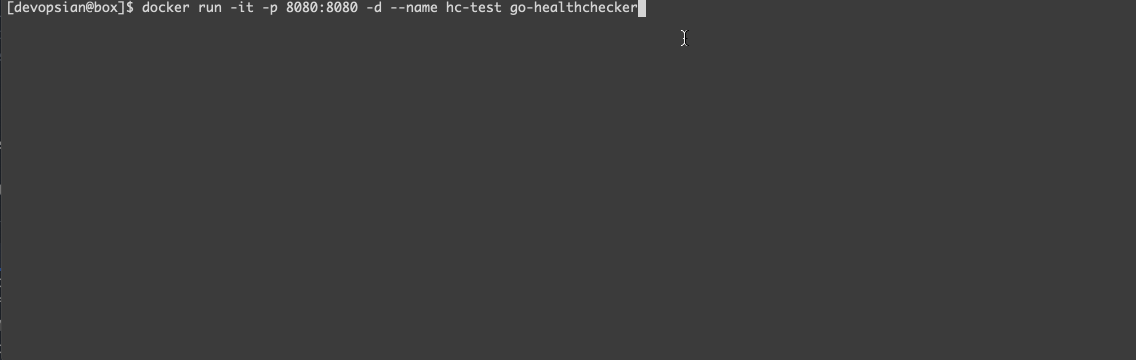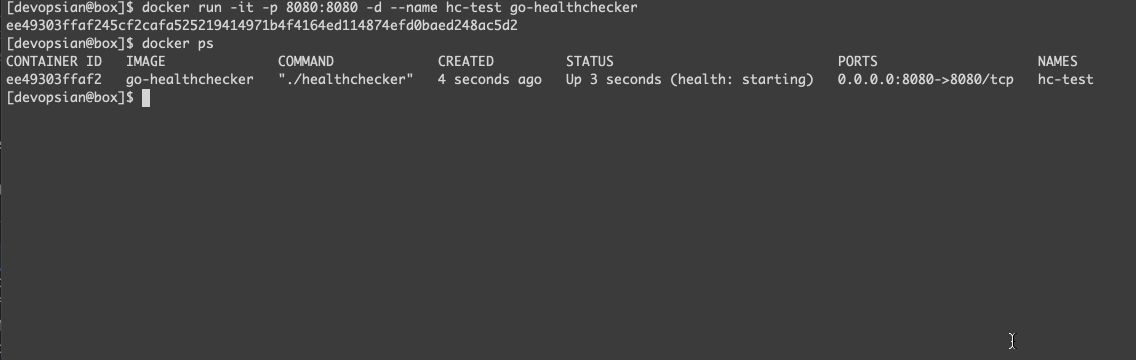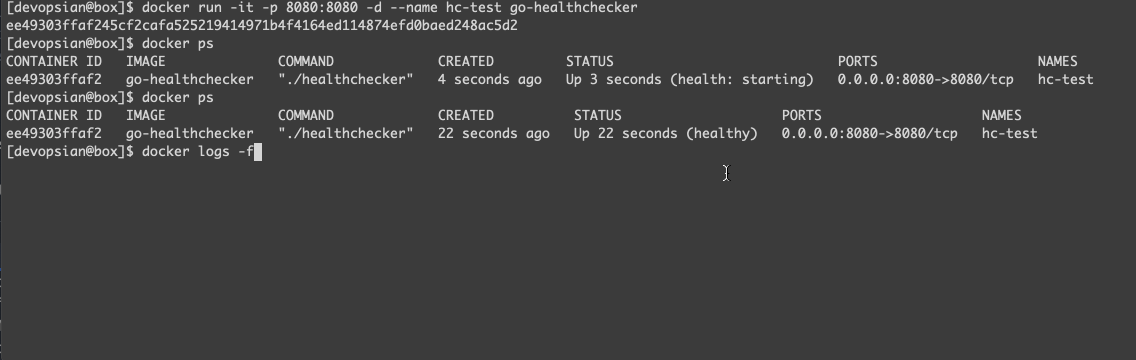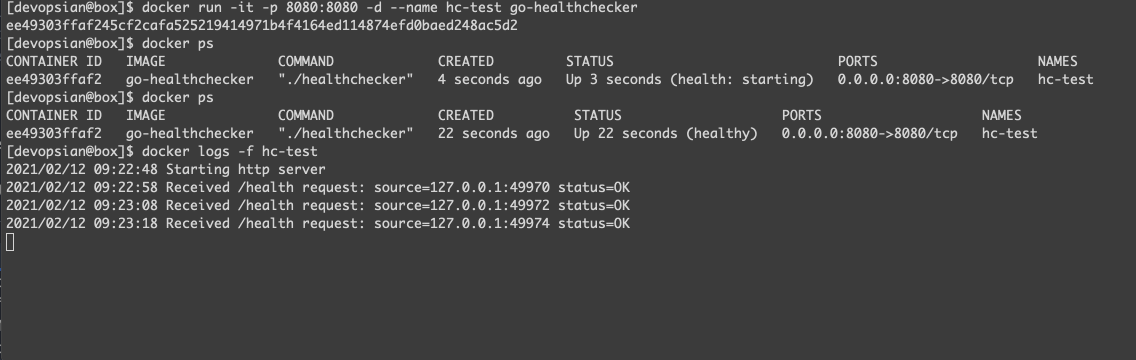
- To change the healthcheck response, connect to the container and update its status

